Homework Statement rewrite the equation in the form of linear equation Then solve it (1x^2)dy/dx xy = 1/ (1x^2) the ans given is y= x/ (1x^2) C / ( sqrt rt (1x^2) ) , my ans is different , which part is wrong ? dy y2 1 = dx Integrating both sides arctan(y) = x C then y = tan(x C) Now, observing the initial condition y(1) = tan(1 C) = 0 so 1 C = 0 kπ,k = ± 1, ± 2,⋯ and concluding 21 (xy)^2 dx(2xyx^21)dy=0, y(1)=1 Ecuaciones exactas Alexander Estrada

Consider The Initial Value Problem Dy Dx 2xy X Chegg Com
X y 2 dx 2xy x 2-1 dy 0 y 1 1
X y 2 dx 2xy x 2-1 dy 0 y 1 1-This is my differential equations practice #12 Give it a try first and check the final answer For differential equations problems requests, just c0 votes 1 answer Solve the following differential equations √(1 x^2 y^2 x^2y^2) xy(dy/dx) = 0



1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 2 2 X 2 1 Youtube
Find the particular solution of the differential equation (1 y^2)(1 log x)dx 2xy dy = 0 given that y = 0 when x = 1 asked May 13 in Differential Equations by Rachi (Learn how to solve differential equations problems step by step online Solve the differential equation xy*dx(1x^2)dy=0 Grouping the terms of the differential equation Group the terms of the differential equation Move the terms of the y variable to the left side, and the terms of the x variable to the right side Simplify the expression \frac{1}{y}dy Integrate both sides of theHomework Equations The Attempt at a Solution
Answered 9 months ago Author has 428 answers and 956K answer views 2xy dx (x^2 1) dy =0 => 2xydx = (x^2–1)dy => 2x/ (x^2–1)dx = dy/y after integrating both sides => ln (x^2–1) = ln (y) constant => ln (x^2–1)ln (y) = constant => ln {y (x^2–1)} = ln (c) ln (c) = constant2xy9x^2(2yx^21)\frac{dy}{dx}=0, y(0)=3 es Related Symbolab blog posts Advanced Math Solutions – Ordinary Differential Equations Calculator, Bernoulli ODE Last post, we learned about separable differential equations In this post, we will learn about Bernoulli differential(x 2 y 2) dx 2xy dy = 0 2xy dy = – (x 2 y 2) dx `("d"y)/("d"x) = ((x^2 y^2))/(2xy)` (1) This is a homogeneous differential equation Put y = vx and
\frac{\mathrm dy}{\mathrm dx}=\left(2xy9x^2\left(2yx^21\right)\right) Write ir as (y2xy^3)dx(3x^2y^2x)dy=0 It is exact Write ir as (y 2 x y 3) d x (3 x 2 y 2 x) d y = 0Get an answer for 'solve first grade ecuation with bernoulli dy/dx = (y^22xy)/x^2 general ecuation and particular when y(1)=1' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes Ex 95, 4 show that the given differential equation is homogeneous and solve each of them (𝑥^2−𝑦^2 )𝑑𝑥2𝑥𝑦 𝑑𝑦=0 Step 1 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 (𝑥^2−𝑦^2 )𝑑𝑥2𝑥𝑦 𝑑𝑦=0 2xy dy = − (𝑥^2−𝑦^2 ) dx 2xy dy = (𝑦^2−𝑥^2 ) dx 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑦^2 − 𝑥^2)/2𝑥𝑦 Step 2 Putting F(x, y) = 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 and finding F



1




How Does One Solve 2xy Dx X 2 1 Dy 0 With The Homogeneus Method Quora
Steps for Solving Linear Equation ( x ^ { 3 } y ^ { 2 } ) d x 3 x y ^ { 2 } d y = 0 ( x 3 y 2) d x − 3 x y 2 d y = 0 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 3 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 3 What is the particular solution of the differential equation? Solve the differential equation dy/dx = ((x^2 y^2 3x 3y 2xy 1)/(x^2 y^2 – 3x – 3y 2xy 2)) asked in Differential equations by Nakul01 ( 369k points) differential equations




Engineering Mathematics Notes




Ex 9 5 15 Class 12 Find Solution 2xy Y 2 2x 2 Dy Dx 0 When
Use Euler method y' = 2 x y, y(1) = 2Math\begin{equation}\begin{split}(xy1)^2\dfrac{dy}{dx}=1\end{split}\end{equation}\tag*{}/math To solve this differential equation, the best trickY = 2 3 e x 2 − 1 − 2 1 Explanation We have d x d y − 2 x y = x Which we can Solve the differential equation \frac{dy}{dx} 3yx = 0 for the values x = 0 when y = 1 Solution Review Solve the differential equation d x d y 3 y x = 0 for the values x = 0 when y = 1 Solution Review




For Problems 26 Determine An Integrating Factor Chegg Com



Solve The Differential Equation Xy 2 Y 2 X Chegg Com
View this answer Given 2xy dx(x2−1) dy = 0 2 x y d x ( x 2 − 1) d y = 0 Rewrite 2xy dxx2 dy−1 dy = 0 2 x y d x x 2 d y − 1 d y = 0 Change the sides $$2 xy \ dx x^2 \ dy = 1Question Solve the given initialvalue problem (x y)2dx (2xy x2 − 6) dy = 0, y(1) = 1 This problem has been solved! Best Answer 92% (13 ratings) Given a differential equation of the form Mdx Ndy = 0 it's exact if Nx= My then to solve it we know that there is a solution F (x,y) = C that satisfies t view the full answer



2x Y 1 Dx 2y X 1 Dy 0 Youtube




1 Given The Differential Equation X2 2xy Y2 Dx Y Chegg Com
(x 2 − y 2) = C (x 2 y 2) 2 is the general solution of the differential equation (x 3 − 3 x y 2) d x = (y 3 − 3 x 2 y) d y, where C is a constant Hard View solutionGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Move all terms containing d to the left, all other terms to the right Factor out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF), 'dx' dx(1 y 2 1x 2) = 0 Subproblem 1 Set the factor 'dx' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying dx = 0 Solving dx = 0 Move all terms containing d to the left, all other terms to the right




For The Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Which Of The Following Are True A Solution Is X 2 Y 2 Cx B X 2 Y 2 Cx C X 2 Y 2 X C D Y 0 0



How To Homogeneous Reducible Differential Equation Dy Dx 2x Y 1 X 2y 1 Quora
A solution of the differential equation (dy dx)2 − xdy dx y = 0 is 6 The differential equation corresponding to the equation y2 = a(b − x2) where a, b are constants is 7 If xy = Asinx osx is the solution of the differential equation xd2y dx2 − 5ady dxExact 2xy9x^2 (2yx^21) (dy)/ (dx)=0 \square!# dx/(x^2x) dy/(y^2y) = 0 # with #y(2)=1# Calculus Applications of Definite Integrals Solving Separable Differential Equations 2 Answers




15 The Differential Equation 2xy Dy X2 Y2 1 Dx Determines A A Family Of Circles With Centre On X Axis B A Family Of Circles With Centre On Y Axis



How To Solve 1 X Dy Dx 2xy X 1 X Quora
2xy9x^2(2yx^21)\frac{dy}{dx}=0, y(0)=3 en Related Symbolab blog posts Advanced Math Solutions – Ordinary Differential Equations Calculator, Linear ODE Ordinary differential equations can be a little tricky In a previous post, we talked about a brief overview of The general solution of the differential equation (y^2 – x^3 )dx – xydy = 0 (x ≠ 0) is (where c is a constant of integration) asked in Mathematics by Jagan (211k points) jee mains 19;Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals arctan(x) dx = arccot(y) dy;




How To Solve Show The Differential Equations Are Exact 2xy Y Tany Dx X 2 X Tany 2 Secy 2 2 Dy 0 Te Tx 2x Dx Dt Xe Xt 0 Quora




3x Xy 2 Dx X 3 2y Dy 0 Y 0 2 Dy Dx Chegg Com
X^0 y x^1 y' x^2 y'' = 1; But if I expand the bracket $(xy)^2$ before integrating I will get $$\varnothing_1=\int Mdx=\int (xy)^2dx=\int (x^22xyy^2)dx=\frac{x^3}{3}xy^2x^2y$$ Wich will lead to the solution $$\varnothing=\varnothing_1\varnothing_2=\frac{x^3}{3}xy^2x^2yy=Constant$$ What is the wrong step ?See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Solve the given initialvalue problem (x y) 2 dx (2xy x 2 − 6) dy = 0, y(1) = 1 Expert Answer Who are




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Integrating Factor Novocom Top




1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 2 2 X 2 1 Youtube
Factor out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF), 'dy' dy(7x 2 x 2 y 2x 2 y 2 2 2y) = 0 Subproblem 1 Set the factor 'dy' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying dy = 0 Solving dy = 0 Move all terms containing d to the left, all other terms to the rightMath\text{Use a substitution} \left\{\begin{array}{l} u = \frac{y}{x} \\ y = ux \\ \mathrm dy = u \,\mathrm dx x \,\mathrm du \end{array}\right/math math(xAnswer to Solve the homogeneous equations x^2 dy ( y^2 xy) dx =0 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your




Solved Problems In Differential Equations 2500 Solved Problems In Differential Docsity



The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy 4x 2 0 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Solve the differential equation dy/dx = (y^3 2x^2y)/(x^3 2xy^2) asked in Differential equations by AmanYadav ( 556k points) differential equationsHelp is appreciated Edit Ex 96, 14For each of the differential equations given in Exercises 13 to 15 , find a particular solution satisfy the given condition




Solve X Y 1 Dx 2x 2y 3 Dy 0 Youtube



What Is The Solution Of Homogeneous Equation 2x Y Dx X 2y Dy 0 Quora
Popular Problems Calculus Find dy/dx 2xyy^2=1 2xy − y2 = 1 2 x y y 2 = 1 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (2xy−y2) = d dx (1) d d x ( 2 x y y 2) = d d x ( 1) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps By the Sum Rule, the derivative of 2 x y − y 2 2 x y y 2 with respect to x x is d d x 2Factor out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF), 'd' d(3x 3x 2 y 1y) = 0 Subproblem 1 Set the factor 'd' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying d = 0 Solving d = 0 Move all terms containing d to the left, all other terms to the rightAnswered 3 years ago If we rewrite this differential equation as d y d x = x 2 y 2 2 x 2 then we see that this is a homogeneous firstorder differential equation There is a standard solution for this type of solution, which is as follows Make the substitution y = u x to get that d ( u x) d x = 1 u 2 2



Solve Xy 3 Y Dx 2 X 2y 2 X Y 4 Dy 0 Youtube




Find The Explicit Particular Solution Of The Initial Chegg Com
Allow me to use D for d/dx We have D(xy^2) = 2x Integrate each side with respect to x to get xy^2 = x^2 C (constant of integration) We will assume we are on the interval (0, infinity) here, so x > 0 Divide by x to get y^2 =x C/x, which gives an implicit form of the general solution on (0, infinity)(x y)2dx (2xy x2 − 6) dy = 0, y(1) = 1; To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `(2xy1)dx(2yx1)dy=0`




Solve Y 2 2x 2y Dx 2x 3 Xy Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
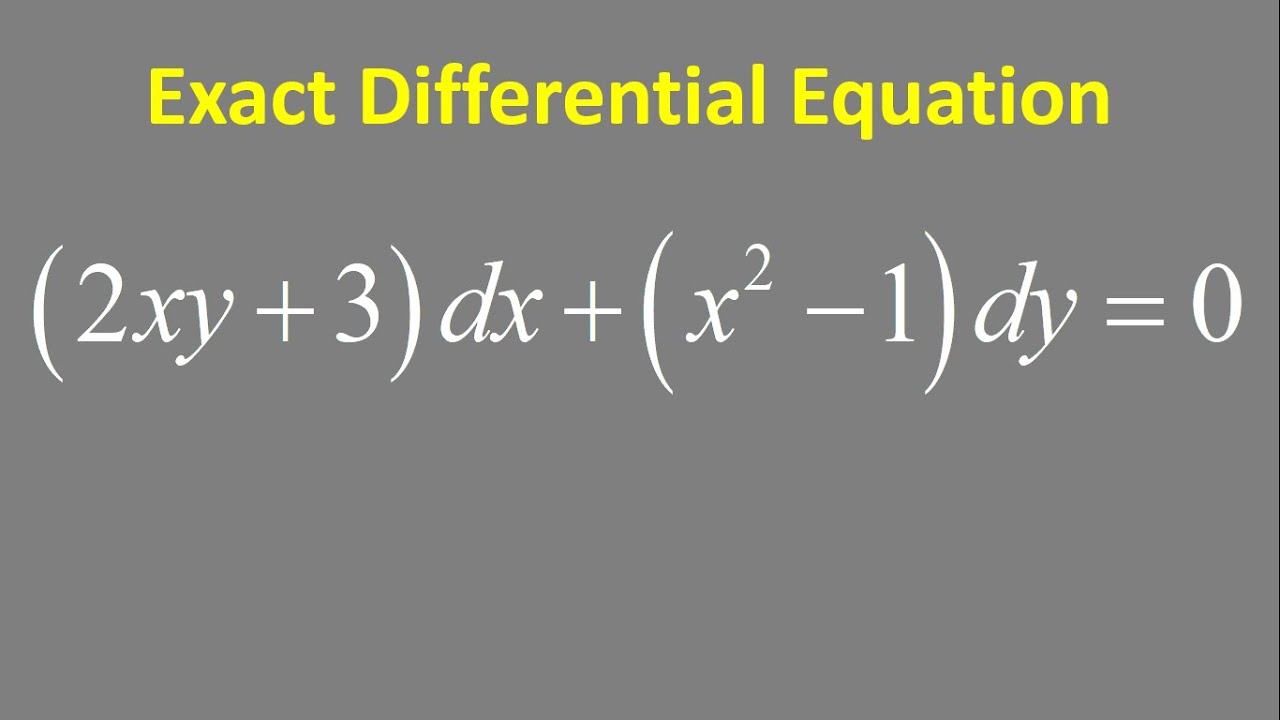



Exact Differential Equation 2xy 3 Dx X 2 1 Dy 0 Youtube
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ The differential equation 2xy dy = x^2 y^2 1 dx determines Join / Login maths The differential equation 2 x y d y = x 2 y 2 1 d x determines A A family of circles with centre on xaxis B A family of circles with centre on yaxis C Put − x 2 1 = d xSimple and best practice solution for (2xy)dx (x^21)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itSet the factor ' (x 2xy 2 2x 2 y y)' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying x 2xy 2 2x 2 y y = 0 Solving x 2xy 2 2x 2 y y = 0 Move all terms containing d to the left, all other terms to the right Add '1x' to each side of the equation x 2xy 2 2x 2 y 1x y = 0 1x Reorder the terms x 1x 2xy 2 2x 2 y



What Is The Solution Of X Y 2 Dx 2xydy 0 Quora




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Novocom Top
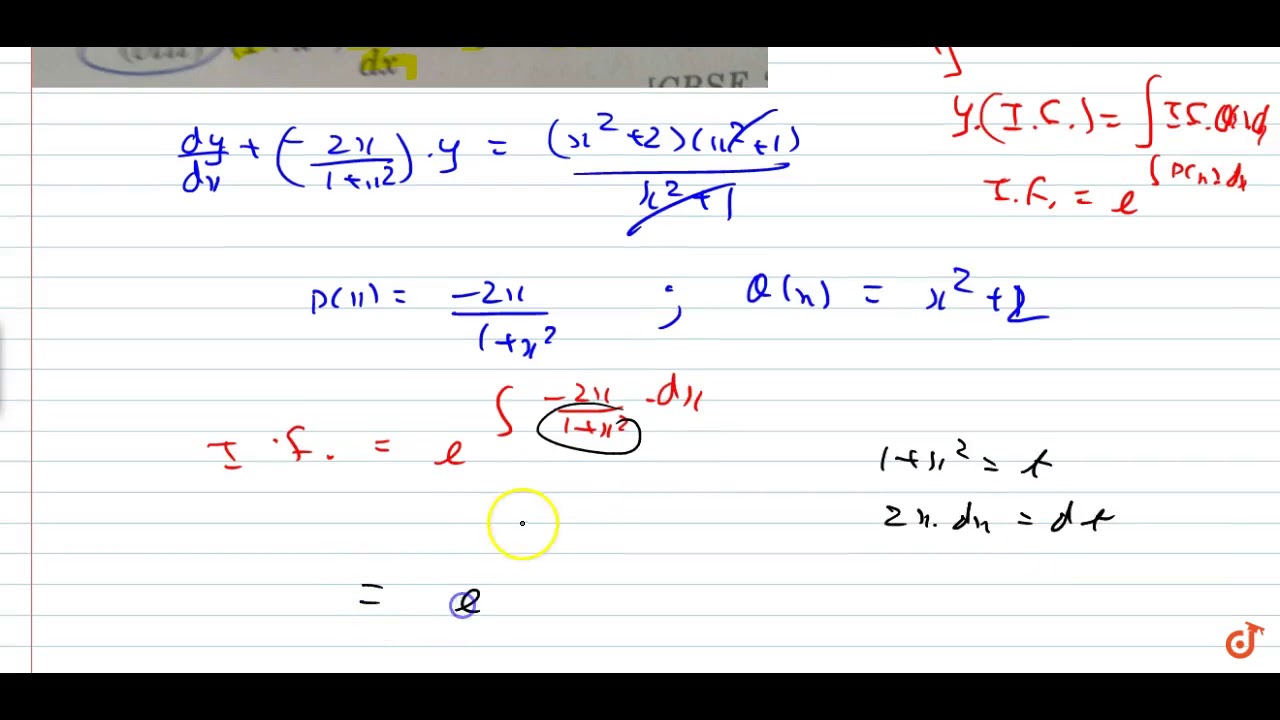
To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `(1x^2)dy/dx2xy=(x^22)(x^21)`



1



Solved Solve The Following Differential Equations X Y 3 Dx X Y 1 Dy 0 2 X Y 1 Dx 3x 4y 2 Dy C 3 1 Y 2 Xy 2 Dx X 2y Y 2xy Dy Course Hero



1




Ex 9 6 8 Find General Solution 1 X2 Dy 2xy Dx Ex 9 6




Consider The Initial Value Problem Dy Dx 2xy X Chegg Com



X Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
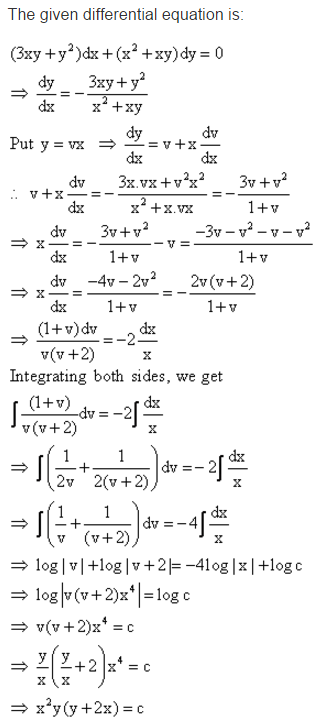



Find The Particular Solution Of Given Differential Equation 3xy Y 2 Dx X 2 Xy Dy 0 At X 1 Y 1 Mathematics Topperlearning Com D1ksg633




In Determine Whether The Given Differential Equation Chegg Com



Solve The Differential Equations 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 1 X 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
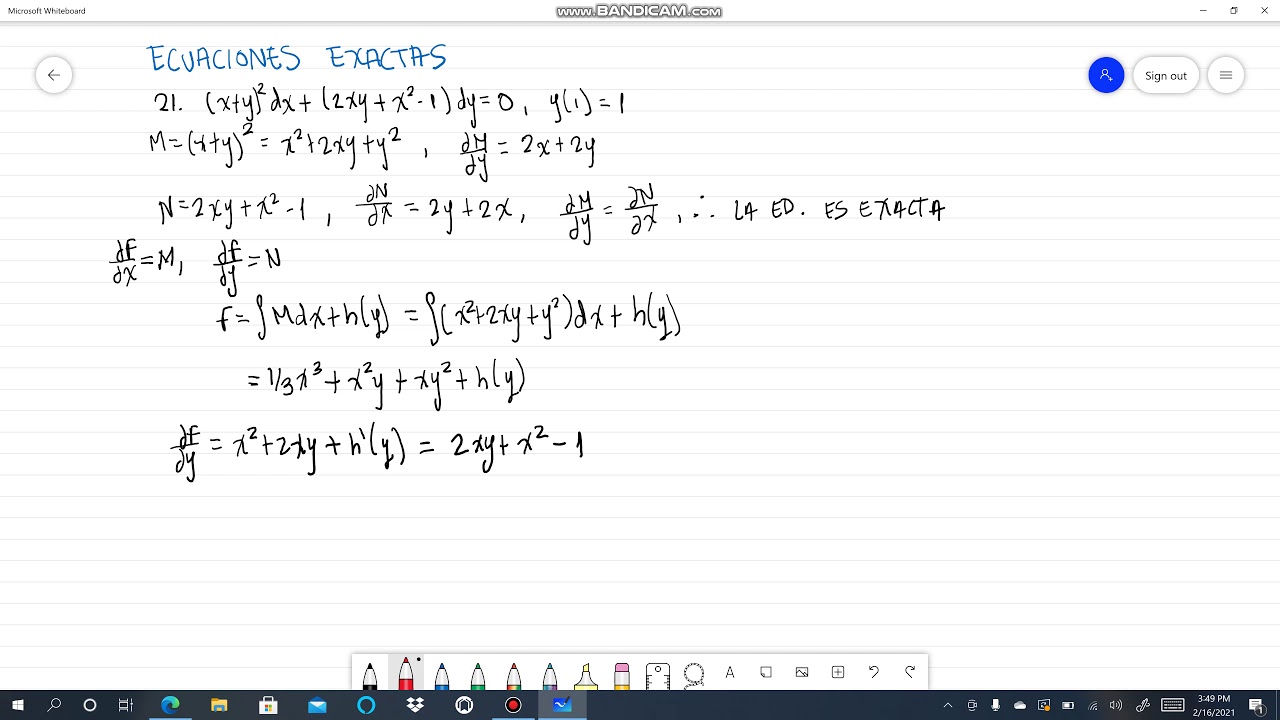



21 X Y 2 Dx 2xy X 2 1 Dy 0 Y 1 1 Ecuaciones Exactas Alexander Estrada Youtube




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Integrating Factor Novocom Top




The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy Xsqrt 1 X 2 0 Is A Y 1 X 2 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 C B Y 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C C Y 1 X 2 3 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C D None Of These




Dy Dx 2xy X Novocom Top




Ex 9 6 14 Find Particular Solution 1 X2 Dy Dx 2xy



How To Solve 2xy Dy Dx X 2 Y 2 Given Y 0 When X 1 Quora




Dy Dx 2xy 2 0 Novocom Top




The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy Xsqrt 1 X 2 0 Is A Y 1 X 2 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 C B Y 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C C Y 1 X 2 3 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C D None Of These




Engineering Mathematics Notes




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Integrating Factor Novocom Top



X Y 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 2 1 Dy Dx Cos 2x Dy Dx Chegg Com




Ecuaciones Diferenciales Homogeneas Xy Y 2 X 2 Dx X 2dy 0 La Prof Lina M3 Youtube




Consider The Following Initial Value Problem X Chegg Com




4 Solve The Exact Differential Equation 1 2xy Dx 4y3 X2 Dy 0 4 Solve The Exact Differential Equation Homeworklib
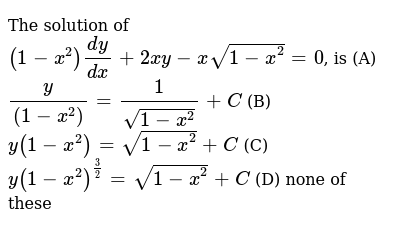



The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy Xsqrt 1 X 2 0 Is A Y 1 X 2 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 C B Y 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C C Y 1 X 2 3 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C D None Of These



Solve The Following Differential Equations 1 3x 2y 4 2xy Dx 2x 3y 3 X 2 Dy 0 Youtube



2xy Y 2 2x 2 Dy Dx 0 Y 2 When X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Novocom Top



Can Anyone Solve This 2x 3y 1 Dx 3x 2y 1 Dy 0 Quora



Answered 3 Y 2 Dx X Y 1 Dy 0 Bartleby
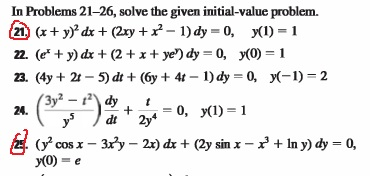



In Problems 21 26 Solve The Given Initial Value Chegg Com



X Y 2 Y 2 Dx X 2 X 2 Y Dy 0 How Do You Solve The Differential Equation Quora




Solve The Given Differentia By Separation Of Chegg Com




Y 3x 1 X 2 2xy Y 2 9 Novocom Top




First Order Differential Equations Chapter 2 Ch2 2 Contents 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 2 Separable Ppt Download



Solve 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 1 X 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




For The Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Which Of The Following Are True Youtube



Solve 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy 4x 2 0 Subject To The Initial Condition Y 0 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Solve The Differential Equation X2 1 Dy Dx 2xy 1 X2 1 Studyrankersonline



Http Fractal Math Unr Edu Ejolson 285 15 Extraprob Pdf
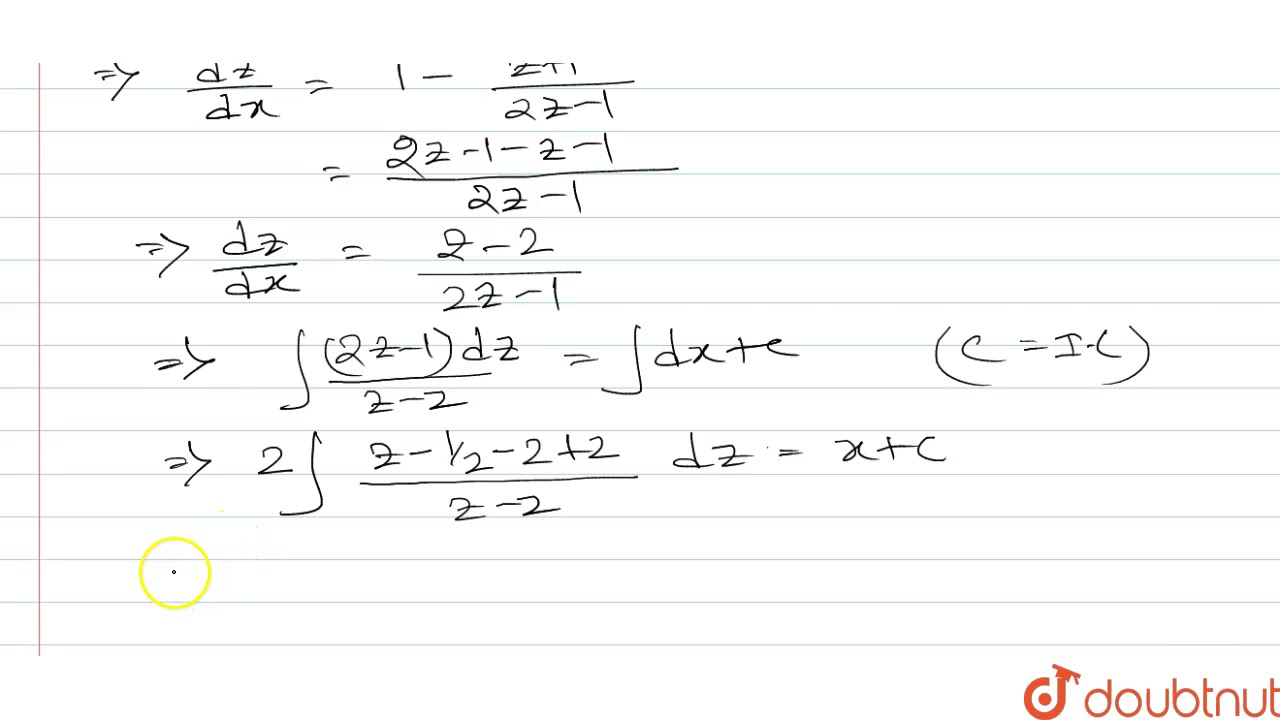



X Y 1 Dx 2x 2y 1 Dy 0 Youtube




The Solution Of The Differential Equation Y Xy 2x 2y 2 Dx X Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Is Given Youtube




Dy Dx 2xy 2 Novocom Top




Dy Dx 2xy 2 0 Novocom Top




Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf




Dy Dx 2xy F X Y 0 2 Novocom Top



Find The Equation Of A Curve Passing Through Origin And Satisfying The Differential Equation 1 X 2dy Dx 2xy 4x2 Studyrankersonline




X2 1 Dy Dx 2xy X4 2x2 1 Cos X Solve This Differential Maths Differential Equations Meritnation Com




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Integrating Factor Novocom Top




Misc 7 Show That General Solution Is X Y 1 A 1 X Y 2xy




Solve The Following Differential Equations Question Chegg Com




Solve The Exact Initial Value Problem 2xy Cos Y Chegg Com




Engineering Mathematics Notes



How To Solve Dy Dx 4x Y 7 2x Y 1 Quora
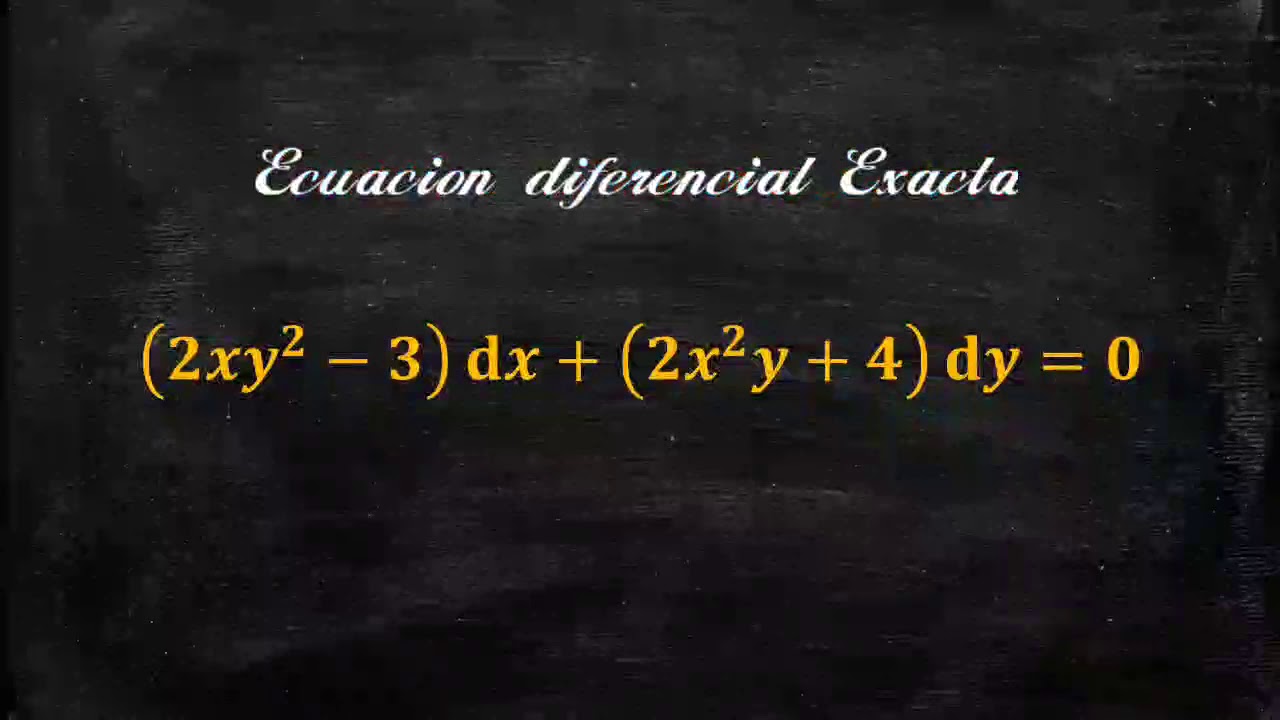



5 2xy 2 3 Dx 2x 2y 4 Dy 0 Ecuacion Diferencial Exacta Youtube
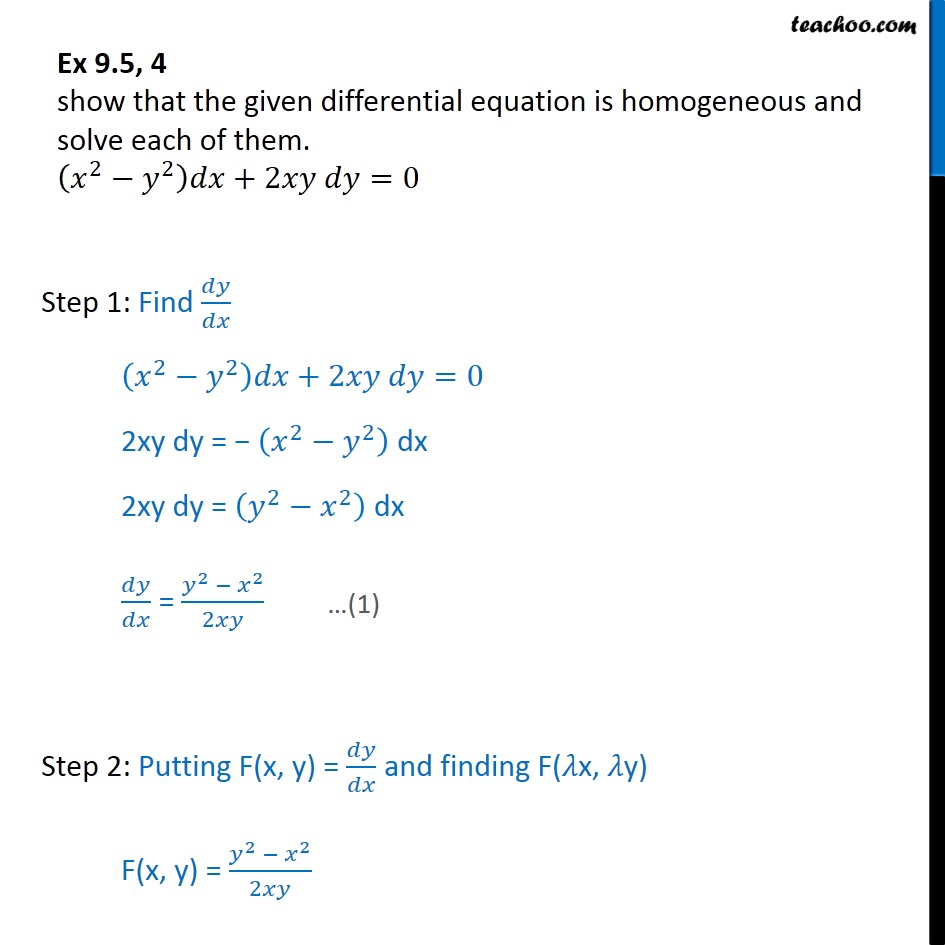



Ex 9 5 4 Show Homogeneous X2 Y2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Ex 9 5




Ex 9 6 14 Find Particular Solution 1 X2 Dy Dx 2xy




Para Verificar Los Problemas 1 Y 2 1 Dx Y Chegg Com



How To Solve The Following Differential Equation 2xy Dx X 2 1 Dy 0 Quora




9 Solve Dy Dx 2xy X 2 Y 2 10 Solve 2xydx 1 Chegg Com




Ex 9 5 4 Show Homogeneous X2 Y2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Ex 9 5




In Solve The Given Initial Value Problem X Y 2 Chegg Com




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



Xy Y Y 2 2x 2xy Y Y 2 Y Dx X Dy 0 X 2 Chegg Com



Solve The Following Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Given That Y 1 When X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Novocom Top




Review Problems In Problems 1 30 Solve The Equation Chegg Com
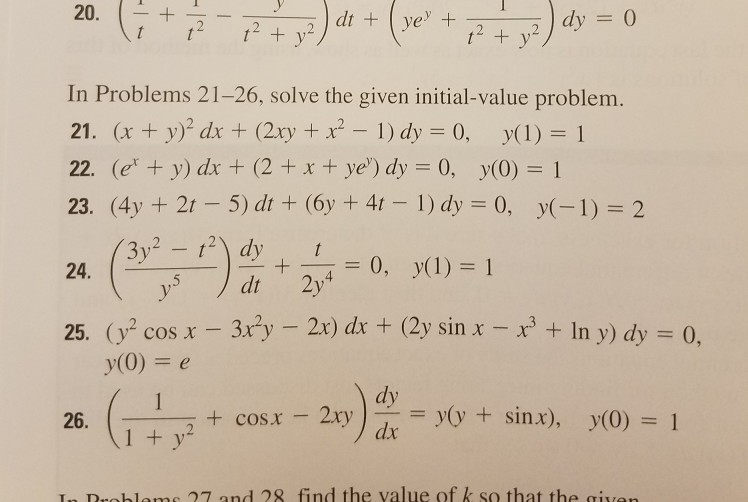



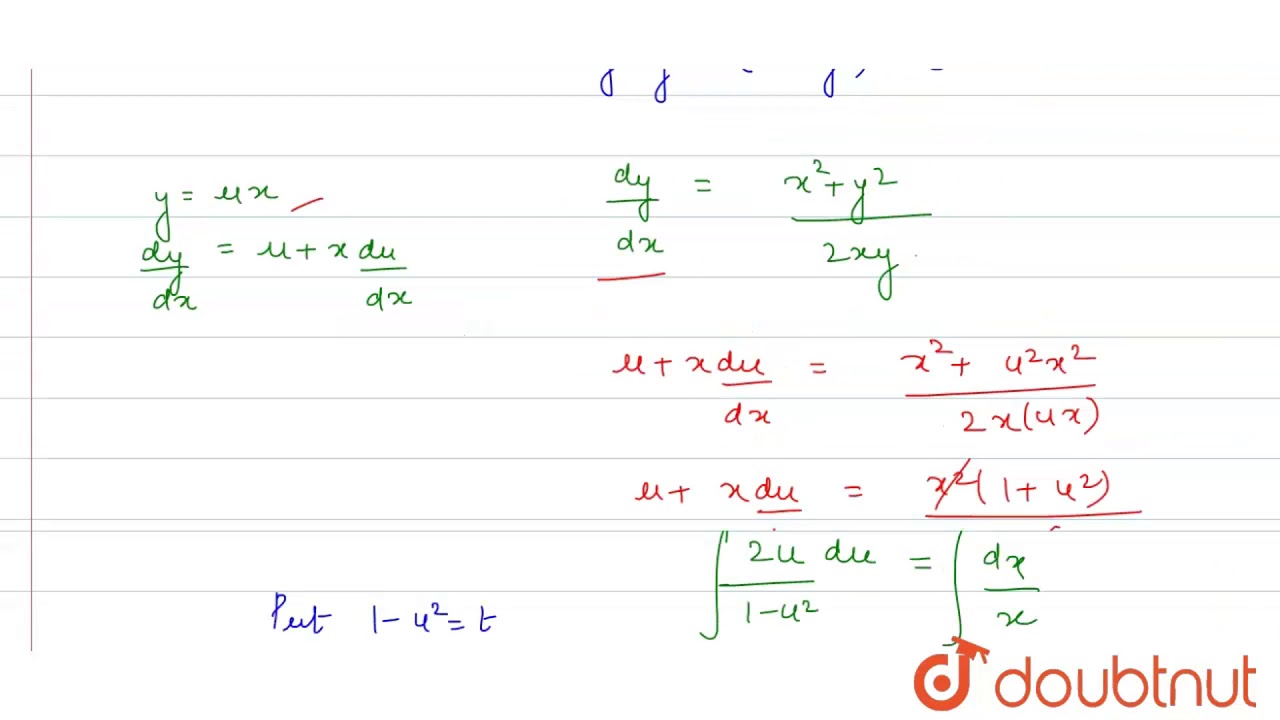
In Problems 21 26 Solve The Given Initial Value Chegg Com



Solve X 2 1 Dy Dx 2xy X 2 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



1




Y 2xy E X Dx E Xdy 0 Novocom Top




Dy Dx 2xy F X Y 0 2 Novocom Top




In Problems 21 26 Solve The Given Initial Value Chegg Com
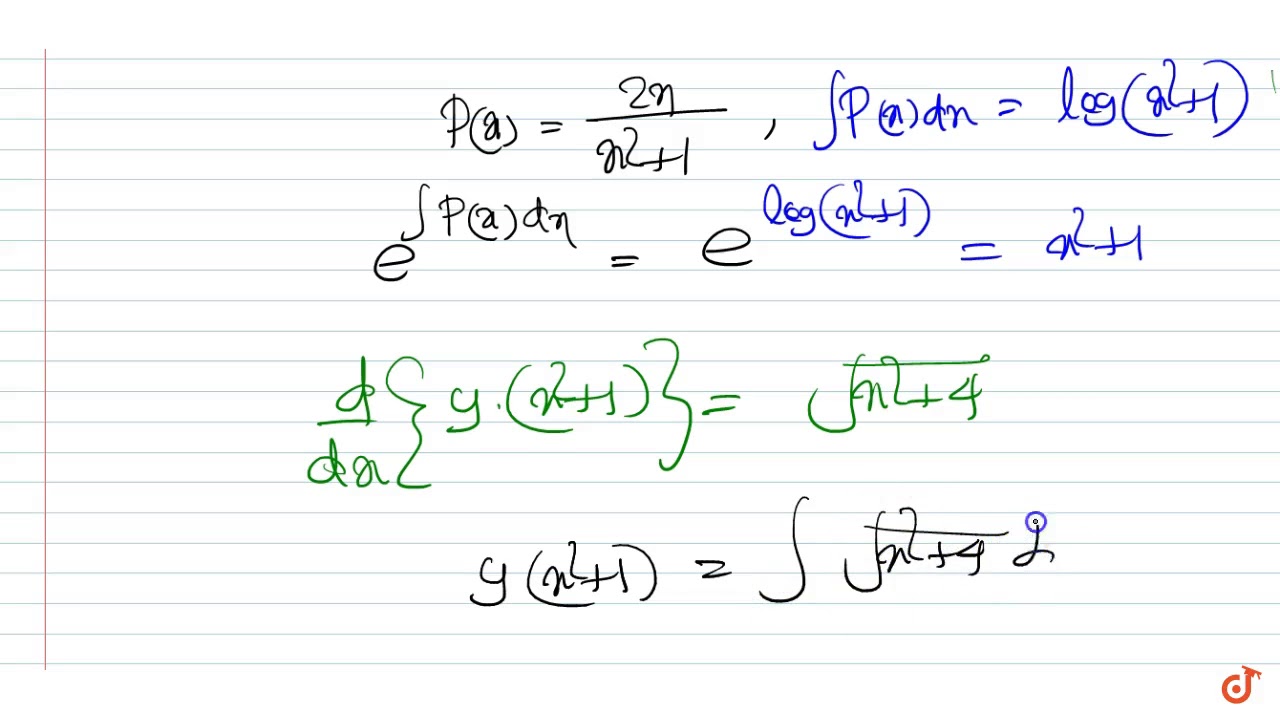



Solve X 2 1 Dy Dx 2xy Sqrt X 2 4 Youtube




The Solution Of Dy Dx X 2 Y 2 1 2xy Satisfying Y 1 0 Is Given By



X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Youtube




Dy Dx 2xy F X Y 0 2 Novocom Top




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions



Solve The Following Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy 1 1 X 2 Given Y 0 When X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


